A Deep Dive into SWIFT Codes: Your Key to International Banking
Author:XTransfer2024-06-06
In the world of international finance, SWIFT codes play a pivotal role. These unique identifiers provide a secure and efficient method for banks across the globe to communicate and facilitate international transactions. This comprehensive guide will uncover the intricacies of SWIFT codes and give you an overview of this unique code.
Decoding the SWIFT Code
A SWIFT code, or a Bank Identifier Code (BIC), is a standardized format of Business Identifier Codes approved by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It's a unique identification code employed for banks and financial institutions around the globe. The SWIFT code is used for inter-bank money transfers, especially international wire transfers, and for message exchanges between banks. You can sometimes find the codes on account statements.
When and Why Should You Use a SWIFT Code?
SWIFT codes come into play during international money transfers. If you're sending money overseas, it's necessary to provide the SWIFT code of the recipient's bank to ensure the funds can reach the correct institution. Banks also use SWIFT codes to exchange messages. Regarding international wire transfers or SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) payments, banks communicate using the SWIFT code to ensure the money ends up in the right place.
The Mechanics of Using a SWIFT Code
Any participant in international financial transactions needs to understand how to use a SWIFT code. Here's a detailed breakdown of the process:
Gathering Information
When you need to make an international wire transfer, you'll require specific details from the recipient:
 |
- Recipient's Name: The full name of the person or business receiving the funds.
- Recipient's Bank Name: The bank's name where the recipient holds their account.
- Recipient's Bank SWIFT Code: The unique SWIFT code identifying the recipient's bank.
- Recipient's Bank Account Number: The account number where the funds will be deposited.
- Recipient's Bank Address (optional):Some banks may require the address of the recipient's bank.
- Amount and Currency: The total amount you wish to transfer and the currency in which it should be sent.
Initiating the Transfer
Once you have gathered all the necessary information, you can initiate the transfer through your bank. This process typically involves the following steps:
 |
- Visit Your Bank: You can go to a branch, use online banking, or access a mobile banking app.
- Fill Out a Transfer Form: Provide the required details, including the recipient's name, bank name, SWIFT code, account number, and the amount to be transferred.
- Specify Payment Details: Indicate the currency and amount and any special instructions for the transfer.
- Review and Confirm: Double-check all the information to ensure accuracy before confirming the transaction.
Processing the Transfer
Once you have submitted the transfer request, your bank will process it through the SWIFT network. Here's how it works:
- Routing the Payment: Your bank sends the payment instructions via the SWIFT network to the recipient's bank using the provided SWIFT code.
- Intermediary Banks: In some cases, intermediary banks may be involved, especially if the sending and receiving banks do not have a direct relationship. These intermediaries help route the payment to the final destination.
- Verification and Compliance: Both the sending and receiving banks verify the transaction details to ensure compliance with international regulations and security protocols.
Receiving the Funds
Once the recipient's bank receives the payment instructions, they will:
- Credit the Recipient's Account: The recipient's bank credits the specified account with the transferred funds.
- Notification: The recipient may receive a notification from their bank confirming the receipt of funds.
Fees and Exchange Rates
Be aware of the following potential costs associated with international wire transfers:
- Transfer Fees: Both the sending and receiving banks may charge fees for processing the transfer. These fees can vary according to different banks and the countries involved.
- Exchange Rates: If the transfer involves currency conversion, the exchange rate applied by the bank may include a margin. It's essential to check the rate to understand how much will be received in the recipient's currency.
The Anatomy of a SWIFT Code
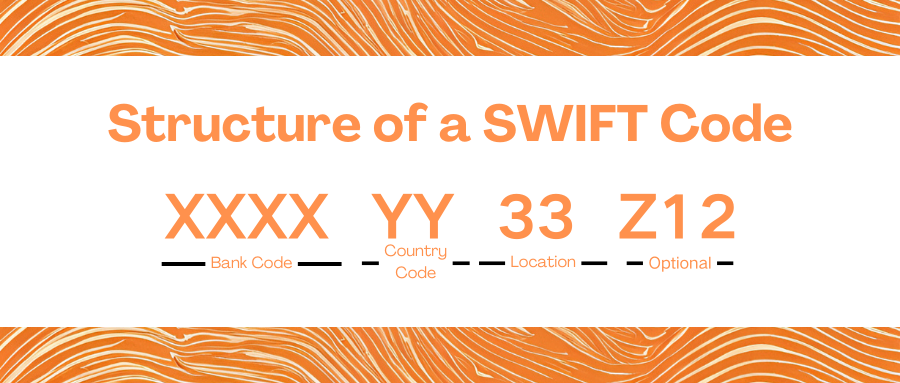
A SWIFT code comprises of 8 or 11 characters and has a specific structure:
- Bank Code: The first 4 characters represent the bank code (us.
- Country Code: The following 2 characters are the country code (signifying the country where the bank is located).
- Location Code: The next 2 characters are the location code (indicating the location of the bank's head office).
- Branch Code: The final 3 characters, which are optional, represent the branch code (identifying a specific branch of the bank).
 |
The Importance of SWIFT Codes in Global Finance
SWIFT codes are not just about facilitating transactions; they are integral to the global financial system. SWIFT codes are crucial to the functioning of the international financial system for several reasons:
1. Standardization and Universality
SWIFT codes provide a standardized and universally accepted system for identifying banks and financial institutions. This standardization simplifies the process of international transactions by ensuring that all participating banks use the same coding structure. It eliminates the confusion that could arise from using different identification methods.
2. Security and Fraud Prevention
The use of SWIFT codes enhances the security of international financial transactions. Each code is unique to a specific bank, reducing the risk of errors and fraud. When funds are transferred using a SWIFT code, the sending and receiving banks can verify each other's identity, ensuring the transaction is legitimate and the funds reach the correct destination.
3. Efficiency and Speed
SWIFT codes facilitate faster processing of international transactions. By providing a clear and precise way to identify banks, SWIFT codes reduce the time spent verifying bank details and processing payments. This efficiency is crucial in the fast-paced world of global finance, where delays can have significant financial implications.
4. Global Reach
With over 11,000 member institutions in more than 200 countries, the SWIFT network has an extensive global reach. This comprehensive coverage means that almost any bank worldwide can be identified and contacted using a SWIFT code, making it an indispensable tool for international business and finance.
 |
5. Cost Reduction
By reducing the need for manual intervention and verification, SWIFT codes help lower the costs associated with international transactions. Banks can process payments faster and with fewer resources, passing on some of these savings to their customers through lower fees.
6. Supporting Financial Messaging
Beyond facilitating payments, SWIFT codes are also used to send various other financial messages between institutions. These messages can include information on securities transactions, treasury transactions, trade services, etc. The reliability and security of SWIFT messaging support a wide range of financial activities beyond simple money transfers.
7. Regulatory Compliance
SWIFT codes help banks comply with international regulations and standards. By using a standardized system, banks can ensure to meet the requirements of regulatory bodies in different countries. This compliance plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the global financial system.
Conclusion
Understanding SWIFT codes is an essential aspect of international banking. Whether you're a business making international payments to suppliers, a family member sending money abroad, or a freelancer receiving payment from overseas clients, you'll likely need to know your bank's SWIFT code. By ensuring you have the correct SWIFT code, you can help ensure your money gets to where it needs to go safely and efficiently.
Despite this comprehensive overview of SWIFT codes, you are advised to consult with your bank or financial institution for specific instructions and information.