Legal Insights on Purchase Contracts in 2025
Author:XTransfer2025.05.30Purchase Contract
A purchase contract is a critical document in any property transaction. It outlines the terms between the buyer and the seller, ensuring both parties understand their obligations. This agreement protects your interests by defining payment details, timelines, and responsibilities. Its legal implications also help prevent disputes and enforce accountability. Whether you're buying or selling, this document provides clarity and reduces risks. For a buyer, it guarantees the property’s condition and delivery. For a seller, it secures payment and limits liability. Understanding this agreement is essential for navigating transactions with confidence.
Understanding Purchase Contracts

Definition and Purpose
A purchase contract is a legally binding document that defines the terms of a transaction between two parties. It ensures that both the buyer and seller understand their rights and obligations. You’ll find key elements like buyer and seller information, payment terms, and delivery deadlines outlined clearly. These details provide structure and clarity, reducing the chances of misunderstandings.
This structure ensures that the agreement is enforceable and protects your interests during the transaction.
Types of Purchase Agreements
Different types of purchase agreements serve specific purposes in transactions. For real estate, a real estate purchase agreement is the most common. It outlines the terms for buying or selling property, including price, contingencies, and deadlines. A purchase and sale agreement is broader, covering various assets like vehicles or equipment. You might also encounter a sales and purchase agreement, which focuses on business transactions.
Each type of agreement plays a unique role in ensuring the transaction proceeds smoothly.
Role in Transactions
Purchase contracts play a vital role in facilitating successful transactions. They provide a structured framework that defines commitments and obligations for both parties. You’ll find critical details like pricing, payment terms, and delivery timelines included. These agreements establish trust and manage risks, ensuring clarity in business relationships.
-
Purchase contracts are legally binding agreements that define the commitments and obligations of both buyers and suppliers, ensuring clarity in business relationships.
-
They provide a structured framework for transactions, which is essential for establishing trust and managing risks.
-
The contracts outline critical details such as scope of work, pricing, payment terms, delivery timelines, and risk management, all of which are vital for successful transaction execution.
Whether you’re buying real estate or negotiating a business deal, a well-drafted purchase contract ensures that both parties fulfill their responsibilities.
Key Components of a Purchase Agreement
Parties Involved
When you enter into a purchase contract, identifying all parties involved is crucial. This includes the buyer, seller, and any agents or representatives. Each party must be listed by their full legal name and address. This ensures proper identification and legal binding. For business entities, using the correct legal designations is essential. This clarity helps avoid confusion and ensures that the contract binds the correct organization.
-
Key Details to Include:
-
Full legal names and contact information of all parties.
-
Proper legal designations for business entities.
-
Roles and responsibilities of each party.
-
Payment Terms and Conditions
Payment terms and conditions form the backbone of any real estate purchase agreement. You need to clearly outline the total price, deposit amounts, and payment schedule. This section should also specify any financing arrangements. By doing so, you ensure that both parties understand their financial obligations. This clarity helps prevent disputes over payments and keeps the transaction on track.
-
Important Elements:
-
Total purchase price and deposit requirements.
-
Payment schedule and financing details.
-
Penalties for late payments or defaults.
-
Contingencies and Warranties
Contingencies and warranties play a vital role in mitigating risks in a real estate purchase agreement. Contingencies are conditions that must be met for the contract to proceed. Common examples include financing approval and satisfactory property inspections. Warranties, on the other hand, provide assurances about the property's condition. They protect you by ensuring that the property meets certain standards.
-
Key Considerations:
-
Include inspection clauses to assess property condition.
-
Use contingencies to address potential conflicts.
-
Understand the role of warranties in minimizing disputes.
-
By understanding these key components of a real estate purchase agreement, you can navigate transactions with confidence. This knowledge helps you protect your interests and ensures a smooth process from start to finish.
Termination Clauses
Termination clauses are essential in any purchase contract. They outline the conditions under which you or the other party can legally end the agreement. These clauses protect both sides by providing a clear exit strategy if specific terms are not met. Without them, disputes can arise, leading to costly legal battles.
Why Termination Clauses Matter
Termination clauses give you control over the agreement. They ensure that you can walk away if the other party fails to meet their obligations. For example, if a seller cannot deliver the property by the agreed deadline, a termination clause allows you to cancel the contract without penalties. These clauses also safeguard your financial interests by preventing unnecessary losses.
Common Grounds for Termination
Termination clauses typically include specific reasons that allow you to end the contract. Here are some common grounds:
-
Failure to Meet Deadlines: If the seller or buyer misses critical deadlines, such as payment or delivery dates, the contract may be terminated.
-
Breach of Contract: Any violation of the agreed terms, like failing to disclose property defects, can trigger termination.
-
Unmet Contingencies: If conditions like financing approval or property inspections are not satisfied, you can exit the agreement.
-
Mutual Agreement: Both parties may agree to terminate the contract without penalties.
Key Elements of a Termination Clause
A well-drafted termination clause should include the following:
How to Use Termination Clauses Effectively
To make the most of termination clauses, you need to understand their implications. Here are some tips:
-
Negotiate Fair Terms: Ensure the conditions for termination are reasonable and protect your interests.
-
Seek Legal Advice: Consult a legal professional to review the clause and confirm it complies with local laws.
-
Document Everything: Keep records of all communications and actions related to the termination. This can help resolve disputes if they arise.
By understanding termination clauses, you can confidently navigate purchase contracts. These provisions provide a safety net, ensuring that you have options if the deal does not go as planned. Always prioritize clarity and fairness when drafting or reviewing these clauses.
Legal Implications of a Purchase Agreement
Enforceability and Validity
The enforceability of a purchase agreement determines whether the contract can be upheld in court. For a contract to be valid, it must meet specific legal requirements. These include mutual consent, a lawful purpose, and consideration (something of value exchanged between the buyer and seller). Without these elements, the agreement may lack legal enforceability.
You should ensure that the purchase agreement contract is clear and complete. Ambiguities can lead to disputes or render the contract unenforceable. For example, in Zwick v. Lodewijk Corp., the court examined the enforceability of non-waiver provisions and oral modifications under the statute of frauds. This case highlights the importance of adhering to written terms and avoiding informal changes. Similarly, the Texas Supreme Court Opinion emphasized the enforceability of liquidated damages provisions in power purchase agreements, treating electricity as a commodity.
To protect your rights, always review the contract for compliance with local laws. Legal enforceability ensures that both parties fulfill their obligations and provides a foundation for resolving disputes.
Breach of Contract Consequences
A breach of contract occurs when one party fails to meet their obligations under the agreement. This can lead to financial losses, legal disputes, and damaged relationships. For example, if a seller fails to deliver the property as agreed, the buyer may lose their earnest money deposit or incur additional costs.
The financial implications of a breach can be significant. Businesses lose an average of 9.2% of their annual revenue due to poor contract management. For every dollar lost in direct revenue, an additional two dollars are lost in compliance fines, legal fees, and productivity loss. These figures underscore the importance of proper contract compliance and management.
-
Common Consequences of Breach:
-
Loss of earnest money deposit.
-
Payment of damages or penalties.
-
Legal fees and court costs.
-
Delays in transaction completion.
-
To minimize risks, you should include clear remedies for breaches in the purchase and sale agreement. These remedies may involve financial compensation, specific performance (forcing the breaching party to fulfill their obligations), or termination of the contract.
Risk Allocation and Liability
Risk allocation defines how risks are shared between the buyer and seller in a purchase agreement. Liability provisions clarify who is responsible for specific issues, such as property defects or delays in delivery. These elements protect your rights and ensure fairness in the transaction.
In real estate purchase agreements, common clauses address risks like property condition, title defects, and financing contingencies. For example, warranties may guarantee that the property meets certain standards, while contingencies allow you to exit the agreement if financing falls through. These clauses reduce uncertainty and provide a safety net for both parties.
Effective risk allocation also involves dispute resolution options. Research shows that alternative dispute resolution (ADR) processes achieve varying success rates depending on the stage of the complaint. At the pre-complaint stage, 55.5% of disputes are resolved, while formal complaint stages see a lower resolution rate of 33.6%. Satisfaction levels also vary, with complainants often expressing dissatisfaction compared to responsible management officials (RMOs).
To allocate risks effectively, you should negotiate terms that balance responsibilities and liabilities. Seek legal guidance to ensure the agreement complies with local laws and protects your interests.
Dispute Resolution Options
Disputes can arise in any transaction, even with a well-drafted purchase agreement. When disagreements occur, you need effective dispute resolution methods to address them. These methods help you avoid prolonged conflicts and costly legal battles. Understanding your options ensures you can resolve issues efficiently and protect your interests.
Common Dispute Resolution Methods
You have several options for resolving disputes in purchase agreements. Each method has its advantages and limitations. Choosing the right one depends on the nature of the disagreement and your goals.
-
Negotiation
Negotiation is often the first step in resolving disputes. It involves direct communication between you and the other party to reach a mutual agreement. This method is informal and cost-effective. You can use negotiation to clarify misunderstandings or propose compromises without involving third parties. -
Mediation
Mediation involves a neutral third party who helps facilitate discussions between you and the other party. The mediator does not make decisions but guides both sides toward a resolution. Mediation works well when both parties are willing to cooperate. It is less formal than arbitration or litigation and often preserves relationships. -
Arbitration
Arbitration is a more formal process where a neutral arbitrator hears both sides and makes a binding decision. This method is faster and less expensive than going to court. However, you must agree to abide by the arbitrator's decision, even if it is not in your favor. -
Litigation
Litigation involves taking the dispute to court. A judge or jury will decide the outcome based on the evidence presented. This method is the most formal and often the most expensive. You might choose litigation for complex disputes or when other methods fail.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Method
Selecting the right dispute resolution method requires careful consideration. You should evaluate the complexity of the issue, the costs involved, and the time required. For example, negotiation and mediation are quicker and less expensive but may not work for serious breaches of the agreement. Arbitration and litigation provide more definitive outcomes but involve higher costs and longer timelines.
Benefits of Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
Alternative dispute resolution methods, such as mediation and arbitration, offer several benefits. They are typically faster and less expensive than litigation. ADR also allows you to maintain privacy, as these processes are not part of the public record. Additionally, ADR methods often preserve business relationships by fostering cooperation and mutual understanding.
Preparing for Dispute Resolution
Preparation is key to resolving disputes effectively. You should gather all relevant documents, such as the purchase agreement and communication records. Understanding the terms of the agreement, including any breach or violation, will strengthen your position. Consulting a legal professional can also help you navigate the process and achieve a favorable outcome.
By exploring your dispute resolution options, you can address conflicts efficiently and protect your interests. Whether you choose negotiation, mediation, arbitration, or litigation, understanding these methods ensures you are prepared for any challenges that arise.
Drafting and Negotiating Purchase Contracts

Ensuring Clarity and Completeness
A clear and complete purchase contract is essential for avoiding misunderstandings and disputes. You should use concise language to ensure all terms are easy to understand. Avoid ambiguity by defining key terms and including detailed descriptions of the property or asset. For example, in a real estate purchase agreement, specify the exact address, dimensions, and any included fixtures.
Standardized processes can help you maintain consistency and completeness. Using templates or preapproved contracts ensures you don’t overlook critical elements. Automation tools also reduce the risk of human error during drafting. Additionally, staying informed about relevant legal requirements ensures your contract remains enforceable.
-
Benefits of clarity and completeness:
-
Standardization ensures consistency across contracts.
-
Quick reference resources speed up the drafting process.
-
Clear language reduces the risk of disputes.
-
Addressing Risks and Contingencies
Addressing risks and contingencies during negotiations protects your interests and reduces the likelihood of disputes. Contingencies allow you to plan for uncertainties, such as financing approval or property inspections. For instance, a real estate purchase agreement often includes clauses that let the buyer exit the contract if the property fails inspection.
You can also use contingent contracts to manage differing views about future events. These agreements include incentives or penalties based on performance, ensuring both parties remain accountable. Including a dispute-resolution clause and negotiating liquidated damages further minimizes risks.
-
Key practices for addressing risks:
-
Include contingency clauses for financing and inspections.
-
Negotiate liquidated damages to handle potential breaches.
-
Add a dispute-resolution clause to streamline conflict resolution.
-
By planning for risks, you create a safety net that protects both the buyer and seller from unforeseen challenges.
Seeking Legal Guidance
Legal guidance is invaluable when drafting and negotiating purchase contracts. A legal professional ensures your contract complies with local laws and includes all necessary provisions. They can also help you navigate complex negotiations, ensuring you achieve favorable terms.
Statistics highlight the importance of legal expertise in contract management. For example:
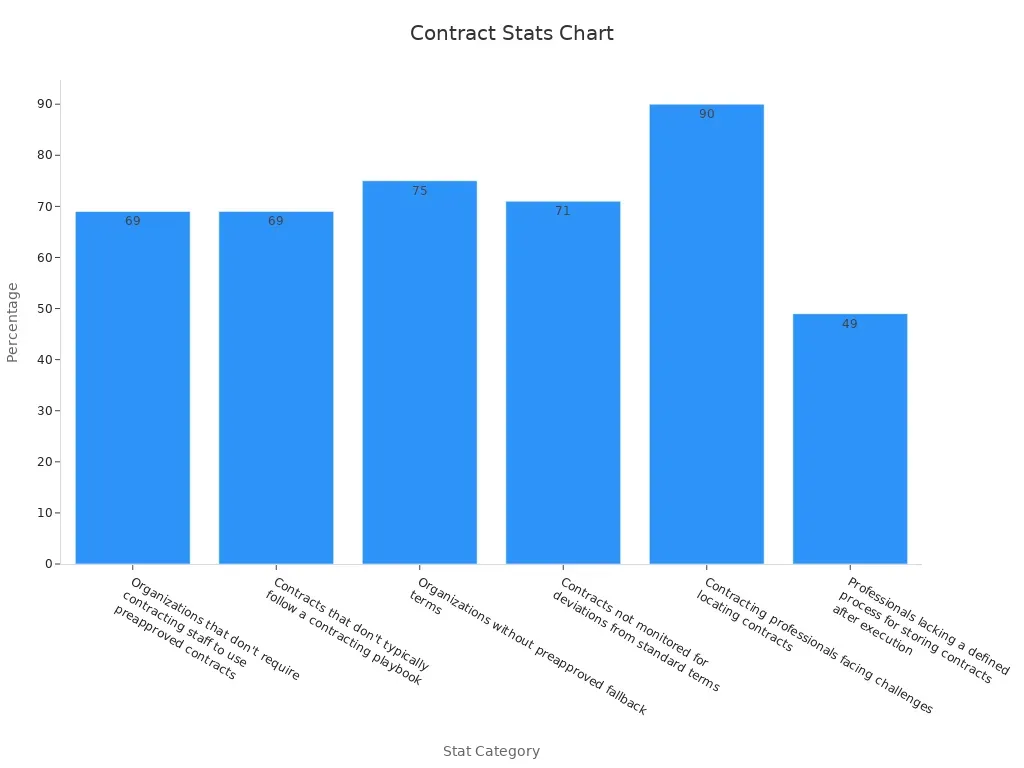
These figures emphasize the risks of poor contract management. Seeking legal advice ensures your contract is thorough, enforceable, and aligned with your goals.
Negotiation Best Practices
Negotiating a purchase contract requires preparation and strategy. A well-executed negotiation ensures that both parties achieve favorable outcomes while maintaining a positive relationship. Whether you are dealing with a real estate purchase agreement or another type of contract, following best practices can help you secure better terms and reduce risks.
Prepare Thoroughly
Preparation is the foundation of successful negotiation. Before entering discussions, you should gather all relevant information about the property, market conditions, and the other party's priorities. For a real estate purchase agreement, this might include reviewing property appraisals, inspection reports, and comparable sales data. Understanding your goals and limits ensures you can negotiate confidently.
Focus on Collaboration
Approaching negotiations with a collaborative mindset often leads to better results. Instead of viewing the other party as an adversary, treat them as a partner in achieving a mutually beneficial agreement. This approach fosters trust and encourages open communication. For example, you might propose creative solutions to address concerns, such as adjusting payment terms or including additional contingencies.
Leverage Data
Using data to support your position strengthens your negotiation strategy. Research shows that companies emphasizing negotiation achieve better outcomes. For instance:
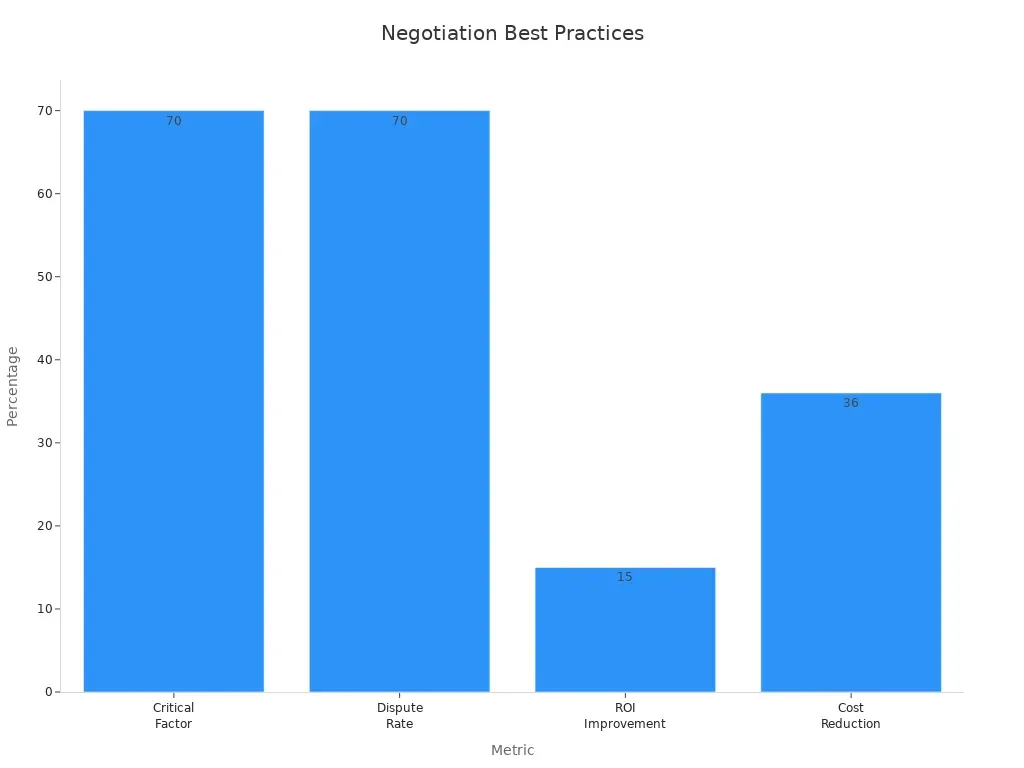
These statistics highlight the importance of negotiation in achieving financial and operational benefits. By presenting data during discussions, you can justify your requests and build credibility.
Stay Flexible
Flexibility is key to overcoming obstacles during negotiations. While you should have clear goals, being open to compromise allows you to adapt to changing circumstances. For example, if the seller in a real estate transaction cannot meet your preferred closing date, you might negotiate a price adjustment instead. Flexibility ensures that you can find solutions that satisfy both parties.
By following these best practices, you can navigate negotiations with confidence. Whether you are finalizing a real estate purchase agreement or another contract, preparation, collaboration, and flexibility will help you achieve your goals.
A purchase contract is essential for ensuring legal clarity and protecting your interests in transactions. It defines the obligations of both the buyer and seller, reducing the risk of disputes. Without a written agreement, misunderstandings can arise, as nearly 45% of professionals have experienced disputes over verbal contracts. Understanding the implications of a purchase agreement contract helps you avoid a breach and ensures smooth transactions. For complex agreements, consulting a legal professional safeguards your rights and ensures compliance with local laws.
FAQ
What makes a purchase contract legally binding?
A purchase contract becomes legally binding when both parties agree to its terms, sign it, and exchange something of value (consideration). Ensure the agreement includes clear terms, mutual consent, and a lawful purpose to avoid disputes.
Can you modify a purchase agreement after signing?
Yes, you can modify it, but both parties must agree to the changes in writing. Always document modifications clearly to avoid misunderstandings or legal challenges later.
What happens if one party breaches the contract?
A breach allows the non-breaching party to seek remedies like financial compensation, specific performance, or contract termination. Review the agreement’s breach clauses to understand your options.
Do you need a lawyer to draft a purchase contract?
While not mandatory, hiring a lawyer ensures your contract complies with laws and protects your interests. Legal guidance is especially helpful for complex agreements or high-value transactions.
How can you resolve disputes without going to court?
You can use alternative dispute resolution methods like mediation or arbitration. These options save time and money while preserving relationships. Check your contract for a dispute resolution clause to guide the process.
Related content