What is the Hong Kong Dollar HKD and Why It Matters
Author:XTransfer2025.08.20HKD
You use the HKD currency every day in Hong Kong for shopping, dining, and business. As Hong Kong’s official currency, it holds a strong position in the world. The HKD currency ranks as the ninth most traded currency globally. This high ranking comes from Hong Kong’s role as a major financial center. Even though trading volume dropped slightly from 8% to 7% after COVID-19, the HKD remains important in global markets.
Highlights
-
The Hong Kong Dollar (HKD) is the official currency of Hong Kong, managed by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA).
-
HKD banknotes and coins come in various denominations with strong security features to help you spot fakes.
-
The HKD uses a pegged exchange rate system linked to the US dollar, keeping its value stable and reliable.
-
The HKMA actively manages the currency to maintain stability, holding large US dollar reserves to support the peg.
-
A stable HKD supports Hong Kong’s role as a global financial center and helps businesses trade and invest with confidence.
What is the HKD Currency?
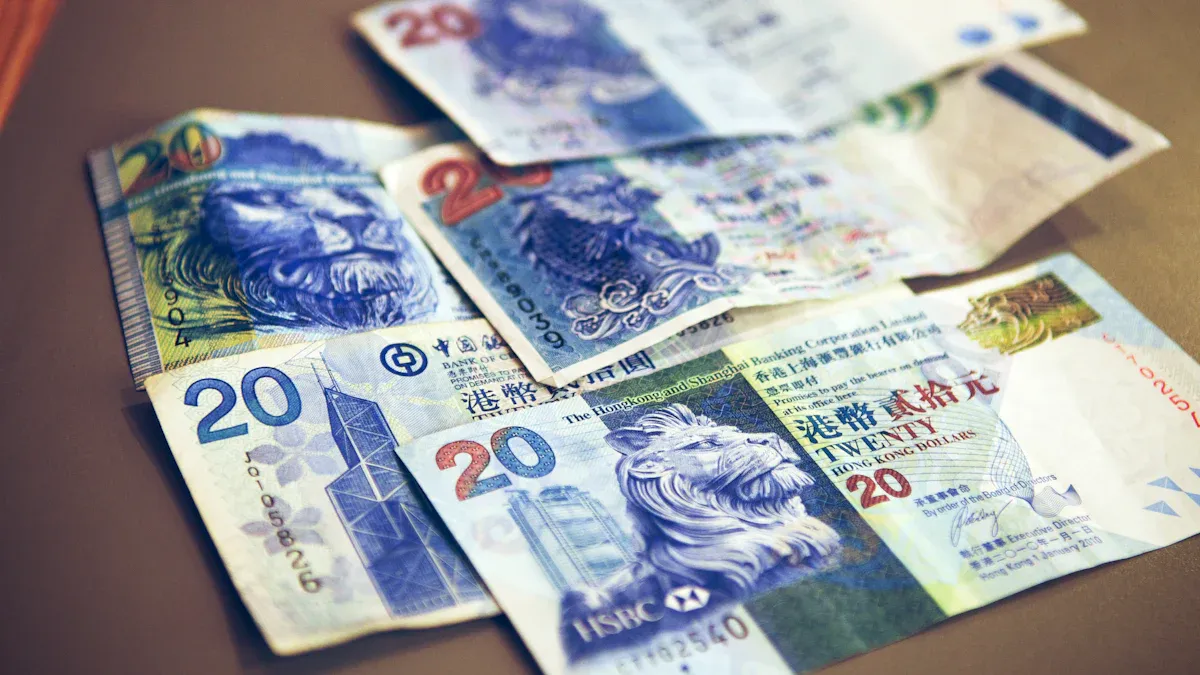

Definition and Symbol
You use the HKD currency every day in Hong Kong. This currency stands as the official money of Hong Kong. The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) manages and issues the HKD currency. You will see the symbol HK$ on price tags, receipts, and banknotes. The international code for the Hong Kong dollar is HKD.
Here is a quick summary:
-
The HKD currency is the official currency of Hong Kong.
-
The symbol is HK$.
-
The ISO code is HKD.
-
The HKMA manages and issues the currency.
Denominations
You will find both coins and banknotes in the HKD currency system. Each type comes in several denominations, making it easy for you to pay for anything from a snack to a new phone.
|
Currency Type |
Denominations in Circulation |
Additional Details |
|
Coins |
10 cents, 20 cents, 50 cents, $1, $2, $5, $10 |
Coins differ in size, color, and edge design. The $10 coin is small but thick with a bronze core and silver rim. |
|
Banknotes |
$10, $20, $50, $100, $500, $1,000 |
Colors vary by denomination. For example, the $10 note comes in green or purple, and the $100 note is red. |
You will notice that the $10 note is special. It comes in both paper and polymer versions. The polymer note has a transparent panel, which helps you check if it is real. All banknotes use strong security features. You can feel raised printing, see-through patterns, and watermarks. These features help you spot fake notes easily.
Issuing Banks
Three major banks issue HKD currency banknotes in Hong Kong. The HKMA authorizes these banks to print and distribute the notes you use every day. The banks are:
-
The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited (HSBC)
-
Bank of China (Hong Kong) Limited
-
Standard Chartered Bank (Hong Kong) Limited
The Hong Kong government issues coins and some banknotes, such as the $10 note. You may notice different designs on banknotes, depending on which bank issued them. All notes, however, have the same value and security features.
HKD Currency System
Pegged Exchange Rate
You may wonder how the HKD currency keeps its value steady. Hong Kong uses a pegged exchange rate system, which means the value of the HKD currency links directly to the US dollar. This system helps keep prices stable and builds trust in the money you use every day.
The peg works through a clear rule. The exchange rate stays close to HK$7.80 for every US$1. The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) promises to keep the rate between HK$7.75 and HK$7.85 per US dollar. If the rate moves too close to either end, the HKMA steps in to fix it. This action keeps the HKD currency from swinging wildly in value.
Here is a simple table to help you understand how the peg works:
|
Aspect |
Description |
|
Exchange Rate System |
Pegged to the US dollar (Linked Exchange Rate System) |
|
Official Pegged Rate |
About HK$7.80 per US$1 |
|
Convertibility Zone |
HK$7.75 (strong side) to HK$7.85 (weak side) per US$1 |
|
Mechanism |
Banks issue HKD only if they deposit equal US dollars with the HKMA |
|
Market Operations |
HKMA buys or sells HKD/USD to keep the rate within the band |
|
Currency Board System |
Every HKD in circulation is backed by US dollar reserves |
This system matters because it removes much of the risk from currency changes. You can trade, invest, or save without worrying that the value of your money will drop overnight. Businesses also benefit because they can plan ahead with more confidence.
Role of HKMA
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority, or HKMA, acts as the guardian of the HKD currency system. You can think of the HKMA as both a currency board and a central bank. Its main job is to keep the peg strong and make sure the financial system runs smoothly.
The HKMA uses several tools to protect the peg and maintain stability:
-
It watches the exchange rate closely. If the HKD gets too strong (closer to HK$7.75), the HKMA sells HKD and buys US dollars. This action adds more HKD to the market and brings the rate back in line.
-
If the HKD gets too weak (closer to HK$7.85), the HKMA buys HKD and sells US dollars. This move takes HKD out of the market and supports its value.
-
The HKMA holds large foreign currency reserves—over US$400 billion. These reserves give the HKMA the power to step in whenever needed.
-
The HKMA adjusts the amount of money in the banking system. When it buys or sells currency, it changes how much money banks have available. This can affect interest rates, which helps control the flow of money in and out of Hong Kong.
The HKMA’s structure is unique. The Financial Secretary of Hong Kong appoints the head of the HKMA, called the Chief Executive. An advisory committee helps guide decisions, making sure the HKMA acts in the best interest of Hong Kong. Unlike some other central banks, the HKMA must always keep enough US dollars to back every HKD in circulation. This rule gives people and businesses extra confidence in the system.
Economists often debate the peg. Many say it anchors trust and removes currency risk. Some worry about the costs, like higher interest rates when the US raises its rates. Still, most agree that the peg remains a key part of Hong Kong’s financial strength.
Importance of HKD

Economic Stability
You benefit from the HKD currency’s stability every day. The peg to the US dollar keeps the value steady, even when the world faces financial crises. This system helps you avoid sudden changes in prices or savings.
-
The peg prevents devaluation during tough times, so you do not lose confidence in your money.
-
In the 1997 Asian financial crisis, many Asian currencies collapsed. Hong Kong’s financial system stayed strong because of the peg.
-
The HKD currency does not change value quickly. Instead, the economy adjusts through inflation or deflation.
-
The government’s promise to keep the peg builds trust and stops currency speculation.
-
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) uses careful supervision and keeps large reserves to protect the system.
Global Financial Center
You see the results of a stable HKD currency in Hong Kong’s global financial status. The city ranks third in the world and first in Asia-Pacific in the Global Financial Centres Index. This high ranking comes from several key factors:
-
The HKMA keeps the exchange rate stable, which gives investors confidence.
-
You can freely convert HKD into other currencies, making international business easy.
-
Hong Kong has no foreign exchange controls. This open market attracts banks and investors from around the world.
-
The city’s financial system is strong, with many top banks and a wide range of investment products.
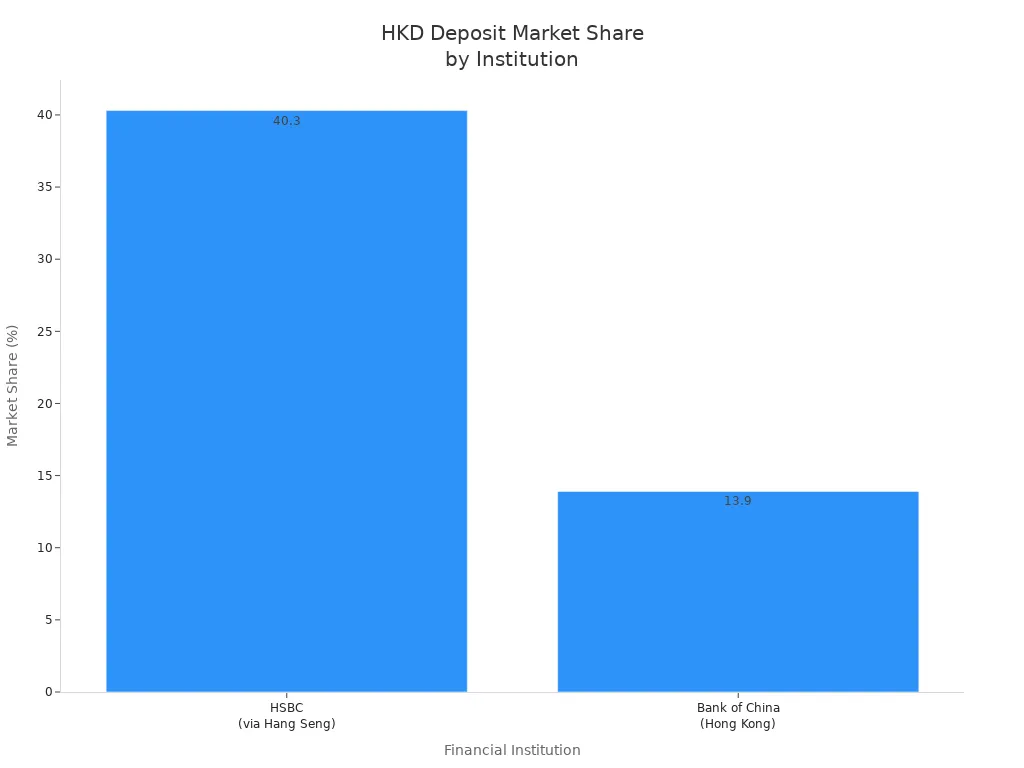
Trade and Investment
You benefit from the HKD currency’s role in trade and investment, both in Hong Kong and across borders. The HKD currency acts as a bridge between China and the rest of the world.
-
The HKD currency is pegged to the US dollar, so it is stable and trusted for trade settlements.
-
Hong Kong is the largest offshore center for the Chinese renminbi (RMB). This makes it easier for you to do business with China.
-
The HKD works with the offshore RMB (CNH) to help companies manage payments to and from China.
-
Hong Kong’s financial infrastructure, like the Dual Counter Model, lets you trade in both HKD and RMB. This gives you more choices and reduces risks.
-
The HKD currency supports free capital movement and helps Hong Kong stay a top place for cross-border investment.
You see how Hong Kong’s financial system stands out in the world.
-
Hong Kong keeps a stable exchange rate and holds large foreign reserves, which supports strong investor confidence.
-
The city’s banking sector remains well-capitalized and resilient, even during global shocks.
-
Hong Kong acts as a gateway between China and global markets, offering deep capital markets and open trade policies.
FAQ
What does HKD stand for?
HKD stands for Hong Kong Dollar. You use this as the official currency in Hong Kong. The symbol is HK$.
Can you use HKD outside Hong Kong?
You can use HKD in Macau and some border cities in China. Most other countries do not accept HKD. You need to exchange it for local money when you travel.
Why do three banks issue HKD banknotes?
Three banks issue HKD banknotes to give you more choices and support a strong financial system. The Hong Kong Monetary Authority checks all notes for safety and value.
How do you check if a HKD banknote is real?
Hold the note up to the light. You will see watermarks, a security thread, and raised printing. These features help you spot fake notes quickly.
Is the HKD exchange rate always the same?
The HKD stays close to HK$7.80 for every US$1. The Hong Kong Monetary Authority keeps the rate between HK$7.75 and HK$7.85. Small changes can happen, but the peg keeps it stable.
Related content